Identity and Access Management Patterns in Cloud-Native Applications
Modern cloud-native applications face unprecedented challenges in managing user identities and controlling access to resources. The traditional perimeter-based security model has given way to sophisticated identity and access management (IAM) patterns that embrace the distributed nature of cloud architectures. Understanding these patterns is crucial for building secure, scalable applications that can adapt to evolving security requirements while maintaining excellent user experiences.
The Evolution of Identity Management
Cloud-native applications operate in environments where traditional network boundaries have dissolved. Users access applications from various devices and locations, while applications themselves consist of numerous microservices communicating across network boundaries. This distributed architecture demands identity management solutions that can provide consistent security policies across all components while maintaining the flexibility needed for modern development practices.
The shift toward cloud-native architectures has fundamentally changed how we approach identity and access management. Instead of relying on network-level controls, modern applications embed identity verification and authorization logic directly into their architecture. This approach ensures that every request is properly authenticated and authorized, regardless of its source or destination within the system.
// Modern identity provider integration using AWS Cognito
import { CognitoIdentityProviderClient, InitiateAuthCommand } from "@aws-sdk/client-cognito-identity-provider";
import { verify } from "jsonwebtoken";
import jwksClient from "jwks-rsa";
interface UserIdentity {
userId: string;
email: string;
groups: string[];
permissions: string[];
tokenExpiry: Date;
}
export class CloudNativeIdentityProvider {
private cognitoClient: CognitoIdentityProviderClient;
private jwksClient: jwksClient.JwksClient;
private userPoolId: string;
private clientId: string;
constructor(userPoolId: string, clientId: string, region: string) {
this.cognitoClient = new CognitoIdentityProviderClient({ region });
this.userPoolId = userPoolId;
this.clientId = clientId;
this.jwksClient = jwksClient({
jwksUri: `https://cognito-idp.${region}.amazonaws.com/${userPoolId}/.well-known/jwks.json`,
cache: true,
cacheMaxAge: 600000, // 10 minutes
rateLimit: true,
jwksRequestsPerMinute: 10
});
}
async authenticateUser(username: string, password: string): Promise<UserIdentity> {
const command = new InitiateAuthCommand({
AuthFlow: "USER_PASSWORD_AUTH",
ClientId: this.clientId,
AuthParameters: {
USERNAME: username,
PASSWORD: password
}
});
try {
const response = await this.cognitoClient.send(command);
if (!response.AuthenticationResult?.AccessToken) {
throw new Error("Authentication failed - no access token received");
}
return await this.validateAndParseToken(response.AuthenticationResult.AccessToken);
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Authentication failed: ${error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error'}`);
}
}
private async validateAndParseToken(token: string): Promise<UserIdentity> {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const decoded = verify(token, this.getSigningKey.bind(this), {
algorithms: ['RS256'],
issuer: `https://cognito-idp.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/${this.userPoolId}`,
audience: this.clientId
}, (err, payload) => {
if (err) {
reject(new Error(`Token validation failed: ${err.message}`));
return;
}
if (typeof payload === 'object' && payload !== null) {
resolve({
userId: payload.sub as string,
email: payload.email as string,
groups: payload['cognito:groups'] as string[] || [],
permissions: this.extractPermissions(payload),
tokenExpiry: new Date((payload.exp as number) * 1000)
});
} else {
reject(new Error("Invalid token payload"));
}
});
});
}
private async getSigningKey(header: any, callback: any) {
this.jwksClient.getSigningKey(header.kid, (err, key) => {
if (err) {
callback(err);
return;
}
const signingKey = key?.getPublicKey();
callback(null, signingKey);
});
}
private extractPermissions(payload: any): string[] {
const groups = payload['cognito:groups'] as string[] || [];
const scopes = payload.scope?.split(' ') || [];
return [...groups.map(group => `group:${group}`), ...scopes];
}
}
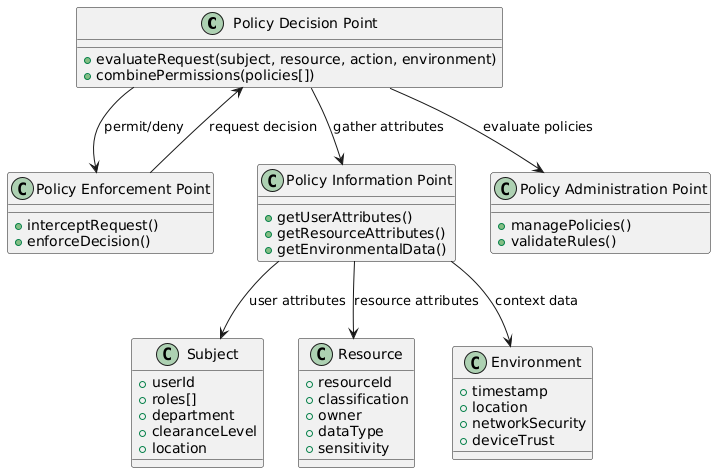
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
Traditional role-based access control (RBAC) systems often prove too rigid for cloud-native applications. Attribute-based access control represents a more flexible approach that considers multiple factors when making authorization decisions. ABAC evaluates user attributes, resource attributes, environmental conditions, and contextual information to determine whether access should be granted.
The power of ABAC lies in its ability to make nuanced decisions based on dynamic conditions. A user might have different levels of access depending on their location, the time of day, the sensitivity of the data they’re requesting, or the security posture of their device. This granular control is essential for applications that handle sensitive data or operate in regulated environments.
// Advanced ABAC implementation for cloud-native applications
interface AccessRequest {
subject: SubjectAttributes;
resource: ResourceAttributes;
action: string;
environment: EnvironmentAttributes;
}
interface SubjectAttributes {
userId: string;
roles: string[];
department: string;
clearanceLevel: number;
location: GeographicLocation;
deviceTrustScore: number;
}
interface ResourceAttributes {
resourceId: string;
classification: DataClassification;
owner: string;
dataTypes: string[];
sensitivity: number;
}
interface EnvironmentAttributes {
timestamp: Date;
sourceIP: string;
networkZone: SecurityZone;
timeOfDay: number;
isBusinessHours: boolean;
}
enum DataClassification {
PUBLIC = 'PUBLIC',
INTERNAL = 'INTERNAL',
CONFIDENTIAL = 'CONFIDENTIAL',
RESTRICTED = 'RESTRICTED'
}
enum SecurityZone {
TRUSTED = 'TRUSTED',
CORPORATE = 'CORPORATE',
DMZ = 'DMZ',
UNTRUSTED = 'UNTRUSTED'
}
interface GeographicLocation {
country: string;
region: string;
city: string;
coordinates: {
latitude: number;
longitude: number;
};
}
export class ABACEngine {
private policies: AccessPolicy[];
private attributeProvider: AttributeProvider;
constructor(attributeProvider: AttributeProvider) {
this.attributeProvider = attributeProvider;
this.policies = this.loadPolicies();
}
async authorize(request: AccessRequest): Promise<AuthorizationResult> {
// Enrich request with additional attributes
const enrichedRequest = await this.enrichRequest(request);
// Evaluate all applicable policies
const policyResults = await Promise.all(
this.policies
.filter(policy => this.isPolicyApplicable(policy, enrichedRequest))
.map(policy => this.evaluatePolicy(policy, enrichedRequest))
);
// Combine results using policy combining algorithm
return this.combineResults(policyResults, enrichedRequest);
}
private async enrichRequest(request: AccessRequest): Promise<AccessRequest> {
// Enhance subject attributes with real-time data
const enhancedSubject = await this.attributeProvider.enrichSubjectAttributes(request.subject);
// Add resource metadata
const enhancedResource = await this.attributeProvider.enrichResourceAttributes(request.resource);
// Calculate environmental context
const enhancedEnvironment = await this.attributeProvider.enrichEnvironmentAttributes(request.environment);
return {
...request,
subject: enhancedSubject,
resource: enhancedResource,
environment: enhancedEnvironment
};
}
private async evaluatePolicy(policy: AccessPolicy, request: AccessRequest): Promise<PolicyResult> {
try {
// Check if user meets minimum requirements
if (!this.checkMinimumRequirements(policy, request)) {
return { decision: 'DENY', reason: 'Minimum requirements not met', policy: policy.id };
}
// Evaluate business rules
const businessRuleResult = await this.evaluateBusinessRules(policy.rules, request);
if (!businessRuleResult.passed) {
return { decision: 'DENY', reason: businessRuleResult.reason, policy: policy.id };
}
// Check temporal constraints
if (!this.checkTemporalConstraints(policy.temporalConstraints, request.environment)) {
return { decision: 'DENY', reason: 'Temporal constraints violated', policy: policy.id };
}
// Evaluate risk factors
const riskScore = await this.calculateRiskScore(request);
if (riskScore > policy.maxRiskThreshold) {
return { decision: 'DENY', reason: `Risk score ${riskScore} exceeds threshold`, policy: policy.id };
}
return { decision: 'PERMIT', reason: 'Policy evaluation successful', policy: policy.id };
} catch (error) {
return { decision: 'INDETERMINATE', reason: `Policy evaluation error: ${error}`, policy: policy.id };
}
}
private async calculateRiskScore(request: AccessRequest): Promise<number> {
let riskScore = 0;
// Location-based risk
if (request.environment.networkZone === SecurityZone.UNTRUSTED) {
riskScore += 30;
}
// Time-based risk
if (!request.environment.isBusinessHours) {
riskScore += 15;
}
// Device trust risk
if (request.subject.deviceTrustScore < 0.7) {
riskScore += 25;
}
// Data sensitivity risk
if (request.resource.sensitivity > 7) {
riskScore += 20;
}
// Cross-border access risk
const userLocation = request.subject.location;
const resourceLocation = await this.attributeProvider.getResourceLocation(request.resource.resourceId);
if (userLocation.country !== resourceLocation.country) {
riskScore += 10;
}
return Math.min(riskScore, 100); // Cap at 100
}
private checkMinimumRequirements(policy: AccessPolicy, request: AccessRequest): boolean {
// Check clearance level
if (request.subject.clearanceLevel < policy.minimumClearance) {
return false;
}
// Check required roles
const hasRequiredRole = policy.requiredRoles.some(role =>
request.subject.roles.includes(role)
);
if (!hasRequiredRole) {
return false;
}
// Check data classification compatibility
const subjectMaxClassification = this.getMaxClassificationForUser(request.subject);
if (this.compareClassifications(request.resource.classification, subjectMaxClassification) > 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
private checkTemporalConstraints(constraints: TemporalConstraint[], environment: EnvironmentAttributes): boolean {
return constraints.every(constraint => {
switch (constraint.type) {
case 'TIME_OF_DAY':
return environment.timeOfDay >= constraint.startHour && environment.timeOfDay <= constraint.endHour;
case 'BUSINESS_HOURS':
return environment.isBusinessHours === constraint.required;
case 'EXPIRY':
return environment.timestamp <= constraint.expiryDate;
default:
return true;
}
});
}
private combineResults(results: PolicyResult[], request: AccessRequest): AuthorizationResult {
// Implement deny-overrides combining algorithm
const denyResults = results.filter(r => r.decision === 'DENY');
if (denyResults.length > 0) {
return {
decision: 'DENY',
reason: denyResults[0].reason,
riskScore: 0,
additionalMeasures: []
};
}
const permitResults = results.filter(r => r.decision === 'PERMIT');
if (permitResults.length > 0) {
return {
decision: 'PERMIT',
reason: 'Access granted by applicable policies',
riskScore: 0,
additionalMeasures: this.determineAdditionalMeasures(request)
};
}
return {
decision: 'DENY',
reason: 'No applicable policies found',
riskScore: 0,
additionalMeasures: []
};
}
private determineAdditionalMeasures(request: AccessRequest): SecurityMeasure[] {
const measures: SecurityMeasure[] = [];
// Require MFA for sensitive operations
if (request.resource.sensitivity > 8) {
measures.push({
type: 'MFA_REQUIRED',
description: 'Multi-factor authentication required for highly sensitive resource'
});
}
// Add monitoring for unusual access patterns
if (request.environment.networkZone !== SecurityZone.TRUSTED) {
measures.push({
type: 'ENHANCED_MONITORING',
description: 'Enhanced monitoring enabled for non-trusted network access'
});
}
return measures;
}
}
Just-In-Time Access Patterns
Just-in-time (JIT) access represents a paradigm shift from permanent privilege assignment to temporary, context-aware access grants. This approach significantly reduces the attack surface by ensuring that users only have access to resources when they specifically need them and only for the duration required to complete their tasks.
Implementing JIT access requires sophisticated orchestration of identity providers, approval workflows, and automated provisioning systems. The architecture must be capable of rapidly granting access based on predefined criteria while maintaining comprehensive audit trails and automatic revocation mechanisms.
// Just-in-time access orchestration system
interface AccessRequest {
requestId: string;
userId: string;
resourceId: string;
justification: string;
requestedDuration: number; // in minutes
urgency: UrgencyLevel;
businessJustification: string;
}
enum UrgencyLevel {
LOW = 'LOW',
MEDIUM = 'MEDIUM',
HIGH = 'HIGH',
CRITICAL = 'CRITICAL'
}
interface ApprovalWorkflow {
workflowId: string;
requiredApprovers: string[];
autoApprovalCriteria?: AutoApprovalCriteria;
escalationRules: EscalationRule[];
}
interface AutoApprovalCriteria {
maxDuration: number;
allowedResources: string[];
allowedUsers: string[];
timeWindows: TimeWindow[];
}
export class JITAccessOrchestrator {
private accessRequests: Map<string, AccessRequest> = new Map();
private activeGrants: Map<string, ActiveGrant> = new Map();
private approvalEngine: ApprovalEngine;
private provisioningService: ProvisioningService;
private auditLogger: AuditLogger;
constructor(
approvalEngine: ApprovalEngine,
provisioningService: ProvisioningService,
auditLogger: AuditLogger
) {
this.approvalEngine = approvalEngine;
this.provisioningService = provisioningService;
this.auditLogger = auditLogger;
// Start background cleanup process
this.startCleanupProcess();
}
async requestAccess(request: AccessRequest): Promise<JITResponse> {
// Validate request
const validation = await this.validateRequest(request);
if (!validation.isValid) {
return {
status: 'REJECTED',
reason: validation.reason,
requestId: request.requestId
};
}
// Store request
this.accessRequests.set(request.requestId, request);
// Log request
await this.auditLogger.logAccessRequest(request);
// Determine approval workflow
const workflow = await this.determineWorkflow(request);
// Check for auto-approval
if (await this.checkAutoApproval(request, workflow)) {
return await this.autoApproveAccess(request);
}
// Initiate approval process
const approvalResult = await this.approvalEngine.initiateApproval(request, workflow);
return {
status: 'PENDING_APPROVAL',
reason: 'Request submitted for approval',
requestId: request.requestId,
expectedApprovalTime: approvalResult.estimatedTime,
approvers: approvalResult.requiredApprovers
};
}
async approveAccess(requestId: string, approverId: string, comments?: string): Promise<JITResponse> {
const request = this.accessRequests.get(requestId);
if (!request) {
return {
status: 'REJECTED',
reason: 'Request not found',
requestId
};
}
// Process approval
const approvalResult = await this.approvalEngine.processApproval(requestId, approverId, true, comments);
if (approvalResult.isComplete && approvalResult.isApproved) {
return await this.grantAccess(request);
}
return {
status: 'PENDING_APPROVAL',
reason: 'Additional approvals required',
requestId,
pendingApprovers: approvalResult.pendingApprovers
};
}
private async autoApproveAccess(request: AccessRequest): Promise<JITResponse> {
try {
const grant = await this.grantAccess(request);
await this.auditLogger.logAutoApproval(request, 'Auto-approval criteria met');
return grant;
} catch (error) {
await this.auditLogger.logError(request.requestId, `Auto-approval failed: ${error}`);
throw error;
}
}
private async grantAccess(request: AccessRequest): Promise<JITResponse> {
try {
// Calculate actual grant duration (may be less than requested)
const grantDuration = await this.calculateGrantDuration(request);
const expiryTime = new Date(Date.now() + grantDuration * 60000);
// Provision access
const provisioningResult = await this.provisioningService.grantAccess({
userId: request.userId,
resourceId: request.resourceId,
permissions: await this.determinePermissions(request),
expiryTime
});
// Create active grant record
const activeGrant: ActiveGrant = {
grantId: provisioningResult.grantId,
requestId: request.requestId,
userId: request.userId,
resourceId: request.resourceId,
grantedAt: new Date(),
expiresAt: expiryTime,
permissions: provisioningResult.permissions,
autoRevoke: true
};
this.activeGrants.set(activeGrant.grantId, activeGrant);
// Schedule automatic revocation
this.scheduleRevocation(activeGrant);
// Log successful grant
await this.auditLogger.logAccessGrant(activeGrant);
return {
status: 'GRANTED',
reason: 'Access successfully granted',
requestId: request.requestId,
grantId: activeGrant.grantId,
expiresAt: expiryTime,
permissions: provisioningResult.permissions
};
} catch (error) {
await this.auditLogger.logError(request.requestId, `Access grant failed: ${error}`);
return {
status: 'REJECTED',
reason: `Failed to grant access: ${error}`,
requestId: request.requestId
};
}
}
private async calculateGrantDuration(request: AccessRequest): Promise<number> {
// Get policy-defined maximum duration for this resource
const maxDuration = await this.getMaxDurationForResource(request.resourceId);
// Consider urgency level
const urgencyMultiplier = this.getUrgencyMultiplier(request.urgency);
const adjustedMaxDuration = maxDuration * urgencyMultiplier;
// Return the minimum of requested duration and policy maximum
return Math.min(request.requestedDuration, adjustedMaxDuration);
}
private getUrgencyMultiplier(urgency: UrgencyLevel): number {
switch (urgency) {
case UrgencyLevel.LOW: return 0.5;
case UrgencyLevel.MEDIUM: return 0.75;
case UrgencyLevel.HIGH: return 1.0;
case UrgencyLevel.CRITICAL: return 1.5;
default: return 0.75;
}
}
private scheduleRevocation(grant: ActiveGrant): void {
const timeUntilExpiry = grant.expiresAt.getTime() - Date.now();
setTimeout(async () => {
await this.revokeAccess(grant.grantId, 'Automatic expiration');
}, timeUntilExpiry);
}
async revokeAccess(grantId: string, reason: string): Promise<void> {
const grant = this.activeGrants.get(grantId);
if (!grant) {
throw new Error(`Grant ${grantId} not found`);
}
try {
// Revoke access in the target system
await this.provisioningService.revokeAccess(grantId);
// Remove from active grants
this.activeGrants.delete(grantId);
// Log revocation
await this.auditLogger.logAccessRevocation(grant, reason);
} catch (error) {
await this.auditLogger.logError(grantId, `Revocation failed: ${error}`);
throw error;
}
}
private startCleanupProcess(): void {
// Run cleanup every 5 minutes
setInterval(async () => {
const now = new Date();
const expiredGrants = Array.from(this.activeGrants.values())
.filter(grant => grant.expiresAt <= now);
for (const grant of expiredGrants) {
try {
await this.revokeAccess(grant.grantId, 'Cleanup process - expired grant');
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Failed to cleanup expired grant ${grant.grantId}:`, error);
}
}
}, 5 * 60 * 1000); // 5 minutes
}
async getActiveGrants(userId?: string): Promise<ActiveGrant[]> {
const grants = Array.from(this.activeGrants.values());
return userId ? grants.filter(grant => grant.userId === userId) : grants;
}
async extendAccess(grantId: string, additionalMinutes: number, justification: string): Promise<JITResponse> {
const grant = this.activeGrants.get(grantId);
if (!grant) {
return {
status: 'REJECTED',
reason: 'Grant not found',
requestId: grantId
};
}
// Check if extension is allowed
const maxExtension = await this.getMaxExtensionForResource(grant.resourceId);
if (additionalMinutes > maxExtension) {
return {
status: 'REJECTED',
reason: `Extension exceeds maximum allowed duration of ${maxExtension} minutes`,
requestId: grantId
};
}
// Extend the grant
const newExpiryTime = new Date(grant.expiresAt.getTime() + additionalMinutes * 60000);
grant.expiresAt = newExpiryTime;
// Update the provisioning system
await this.provisioningService.extendAccess(grantId, newExpiryTime);
// Log the extension
await this.auditLogger.logAccessExtension(grant, additionalMinutes, justification);
return {
status: 'GRANTED',
reason: 'Access successfully extended',
requestId: grantId,
expiresAt: newExpiryTime
};
}
}
Token-Based Authentication Strategies
Modern cloud-native applications rely heavily on token-based authentication mechanisms that provide stateless, scalable identity verification. JSON Web Tokens (JWT) have become the de facto standard for representing claims securely between parties, but their implementation requires careful consideration of security best practices and architectural patterns.
The evolution of token strategies has moved beyond simple bearer tokens to sophisticated patterns that include refresh token rotation, proof-of-possession tokens, and context-aware token validation. These advanced patterns provide enhanced security while maintaining the performance and scalability benefits that make tokens attractive for distributed systems.
// Advanced token management system with security best practices
interface TokenClaims {
sub: string; // Subject (user ID)
iss: string; // Issuer
aud: string; // Audience
exp: number; // Expiration time
iat: number; // Issued at
jti: string; // JWT ID (unique identifier)
scope: string; // Permissions scope
device_id?: string; // Device identifier
session_id?: string; // Session identifier
risk_score?: number; // Risk assessment score
}
interface TokenPair {
accessToken: string;
refreshToken: string;
tokenType: string;
expiresIn: number;
scope: string;
}
interface DeviceInfo {
deviceId: string;
deviceType: string;
platform: string;
appVersion: string;
deviceFingerprint: string;
}
export class SecureTokenManager {
private readonly accessTokenTTL = 15 * 60; // 15 minutes
private readonly refreshTokenTTL = 7 * 24 * 60 * 60; // 7 days
private readonly maxRefreshTokens = 5; // Per user
private tokenBlacklist: Set<string> = new Set();
private refreshTokenStore: Map<string, RefreshTokenInfo> = new Map();
constructor(
private jwtSecret: string,
private issuer: string,
private audience: string,
private encryptionKey: string
) {
// Start cleanup process for expired tokens
this.startTokenCleanup();
}
async generateTokenPair(
userId: string,
scope: string,
deviceInfo: DeviceInfo,
riskScore: number = 0
): Promise<TokenPair> {
// Generate unique identifiers
const jti = this.generateSecureId();
const sessionId = this.generateSecureId();
const refreshTokenId = this.generateSecureId();
// Create access token claims
const accessTokenClaims: TokenClaims = {
sub: userId,
iss: this.issuer,
aud: this.audience,
exp: Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000) + this.accessTokenTTL,
iat: Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000),
jti,
scope,
device_id: deviceInfo.deviceId,
session_id: sessionId,
risk_score: riskScore
};
// Generate access token
const accessToken = await this.createSignedToken(accessTokenClaims);
// Create refresh token with encrypted payload
const refreshTokenPayload = {
user_id: userId,
session_id: sessionId,
device_id: deviceInfo.deviceId,
scope,
exp: Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000) + this.refreshTokenTTL,
jti: refreshTokenId
};
const refreshToken = await this.createEncryptedRefreshToken(refreshTokenPayload);
// Store refresh token metadata
await this.storeRefreshToken(refreshTokenId, {
userId,
deviceInfo,
sessionId,
createdAt: new Date(),
expiresAt: new Date(Date.now() + this.refreshTokenTTL * 1000),
lastUsed: new Date(),
isActive: true
});
// Cleanup old refresh tokens for this user/device
await this.cleanupOldRefreshTokens(userId, deviceInfo.deviceId);
return {
accessToken,
refreshToken,
tokenType: 'Bearer',
expiresIn: this.accessTokenTTL,
scope
};
}
async validateAccessToken(token: string, requiredScope?: string): Promise<TokenValidationResult> {
try {
// Check if token is blacklisted
if (this.tokenBlacklist.has(token)) {
return {
isValid: false,
reason: 'Token has been revoked',
claims: null
};
}
// Verify and decode token
const claims = await this.verifySignedToken(token);
// Additional security checks
const securityChecks = await this.performSecurityChecks(claims, token);
if (!securityChecks.passed) {
return {
isValid: false,
reason: securityChecks.reason,
claims: null
};
}
// Check scope if required
if (requiredScope && !this.hasRequiredScope(claims.scope, requiredScope)) {
return {
isValid: false,
reason: 'Insufficient scope',
claims: null
};
}
return {
isValid: true,
reason: 'Token is valid',
claims
};
} catch (error) {
return {
isValid: false,
reason: `Token validation failed: ${error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error'}`,
claims: null
};
}
}
async refreshTokenPair(refreshToken: string, deviceInfo: DeviceInfo): Promise<TokenPair> {
try {
// Decrypt and validate refresh token
const refreshPayload = await this.decryptRefreshToken(refreshToken);
// Get refresh token info from store
const tokenInfo = this.refreshTokenStore.get(refreshPayload.jti);
if (!tokenInfo || !tokenInfo.isActive) {
throw new Error('Refresh token not found or inactive');
}
// Validate device consistency
if (tokenInfo.deviceInfo.deviceId !== deviceInfo.deviceId) {
// Device mismatch - possible token theft
await this.revokeAllUserTokens(tokenInfo.userId, 'Device mismatch detected');
throw new Error('Device validation failed');
}
// Check if refresh token is expired
if (tokenInfo.expiresAt <= new Date()) {
throw new Error('Refresh token expired');
}
// Update last used timestamp
tokenInfo.lastUsed = new Date();
// Calculate new risk score based on usage patterns
const riskScore = await this.calculateRefreshRiskScore(tokenInfo, deviceInfo);
// Generate new token pair
const newTokenPair = await this.generateTokenPair(
tokenInfo.userId,
refreshPayload.scope,
deviceInfo,
riskScore
);
// Optionally rotate refresh token for high-risk scenarios
if (riskScore > 70) {
await this.revokeRefreshToken(refreshPayload.jti);
}
return newTokenPair;
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Token refresh failed: ${error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error'}`);
}
}
private async performSecurityChecks(claims: TokenClaims, token: string): Promise<SecurityCheckResult> {
// Check token age
const tokenAge = Date.now() / 1000 - claims.iat;
if (tokenAge > this.accessTokenTTL) {
return { passed: false, reason: 'Token expired' };
}
// Risk score validation
if (claims.risk_score && claims.risk_score > 90) {
return { passed: false, reason: 'Risk score too high' };
}
// Check for session validity if session management is enabled
if (claims.session_id) {
const sessionValid = await this.validateSession(claims.session_id, claims.sub);
if (!sessionValid) {
return { passed: false, reason: 'Session invalid' };
}
}
// Device binding validation
if (claims.device_id) {
const deviceValid = await this.validateDeviceBinding(claims.device_id, claims.sub);
if (!deviceValid) {
return { passed: false, reason: 'Device binding invalid' };
}
}
return { passed: true, reason: 'All security checks passed' };
}
private async calculateRefreshRiskScore(tokenInfo: RefreshTokenInfo, deviceInfo: DeviceInfo): Promise<number> {
let riskScore = 0;
// Time-based risk factors
const timeSinceLastUse = Date.now() - tokenInfo.lastUsed.getTime();
if (timeSinceLastUse > 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000) { // More than 24 hours
riskScore += 20;
}
// Device fingerprint changes
if (tokenInfo.deviceInfo.deviceFingerprint !== deviceInfo.deviceFingerprint) {
riskScore += 30;
}
// Platform/app version changes
if (tokenInfo.deviceInfo.platform !== deviceInfo.platform) {
riskScore += 40;
}
if (tokenInfo.deviceInfo.appVersion !== deviceInfo.appVersion) {
riskScore += 10;
}
// Frequency analysis
const refreshFrequency = await this.analyzeRefreshFrequency(tokenInfo.userId);
if (refreshFrequency > 10) { // More than 10 refreshes per hour
riskScore += 25;
}
return Math.min(riskScore, 100);
}
async revokeToken(token: string): Promise<void> {
// Add to blacklist
this.tokenBlacklist.add(token);
// If it's a refresh token, mark as inactive
try {
const refreshPayload = await this.decryptRefreshToken(token);
const tokenInfo = this.refreshTokenStore.get(refreshPayload.jti);
if (tokenInfo) {
tokenInfo.isActive = false;
}
} catch {
// Not a refresh token, blacklisting is sufficient
}
}
async revokeAllUserTokens(userId: string, reason: string): Promise<void> {
// Find all refresh tokens for the user
const userTokens = Array.from(this.refreshTokenStore.entries())
.filter(([_, info]) => info.userId === userId);
// Mark all as inactive
for (const [tokenId, info] of userTokens) {
info.isActive = false;
}
// Log security event
console.warn(`Revoked all tokens for user ${userId}: ${reason}`);
}
private startTokenCleanup(): void {
// Run cleanup every hour
setInterval(() => {
this.cleanupExpiredTokens();
}, 60 * 60 * 1000);
}
private cleanupExpiredTokens(): void {
const now = new Date();
// Clean up expired refresh tokens
for (const [tokenId, info] of this.refreshTokenStore.entries()) {
if (info.expiresAt <= now) {
this.refreshTokenStore.delete(tokenId);
}
}
// Clean up old blacklisted access tokens (they expire anyway)
// This would require more sophisticated tracking in a real implementation
}
private async cleanupOldRefreshTokens(userId: string, deviceId: string): Promise<void> {
const userDeviceTokens = Array.from(this.refreshTokenStore.entries())
.filter(([_, info]) => info.userId === userId && info.deviceInfo.deviceId === deviceId)
.sort(([_, a], [__, b]) => b.createdAt.getTime() - a.createdAt.getTime());
// Keep only the most recent tokens up to the limit
const tokensToRemove = userDeviceTokens.slice(this.maxRefreshTokens);
for (const [tokenId] of tokensToRemove) {
this.refreshTokenStore.delete(tokenId);
}
}
}
Conclusion
Identity and access management in cloud-native applications represents a fundamental shift from traditional security models to dynamic, context-aware systems that can adapt to changing threats and business requirements. The patterns explored in this post demonstrate how modern applications can implement sophisticated security controls while maintaining the flexibility and scalability that cloud-native architectures demand.
The implementation of these IAM patterns requires careful consideration of the trade-offs between security, usability, and performance. Attribute-based access control provides the granular control needed for complex authorization decisions but introduces complexity in policy management and evaluation. Just-in-time access patterns significantly reduce security risks by minimizing standing privileges but require robust orchestration and approval systems. Advanced token strategies enhance security through multiple layers of validation and risk assessment while maintaining the stateless nature essential for distributed systems.
As cloud-native applications continue to evolve, IAM systems must adapt to support new architectural patterns, emerging threats, and changing regulatory requirements. Organizations implementing these patterns should focus on creating flexible, extensible systems that can grow with their security needs while providing comprehensive audit capabilities and seamless user experiences. The foundation laid by these identity and access management patterns will prove essential as we explore additional security layers in subsequent posts in this series.
Comments